From the Stockholm Resilience Center:
Today, 60 per cent of the free ecosystem services that we use are exploited in an unsustainable manner.
Crucial ecosystem services such as air- and water purification, the pollination of crops and the seas’ capacity to produce fish are in serious decline. The changes are occurring so rapidly today that society is unable to adapt to the new environmental circumstances and thus cannot effectively develop strategies and frameworks for sustainable use of the ecosystems.
“Our societies are an integrated part of the biosphere and dependent upon functioning ecosystems. That is why we need to manage ecosystems so that we can handle the future’s challenges and maintain our capacity to evolve in a positive way,” says Carl Folke.
With that in mind:
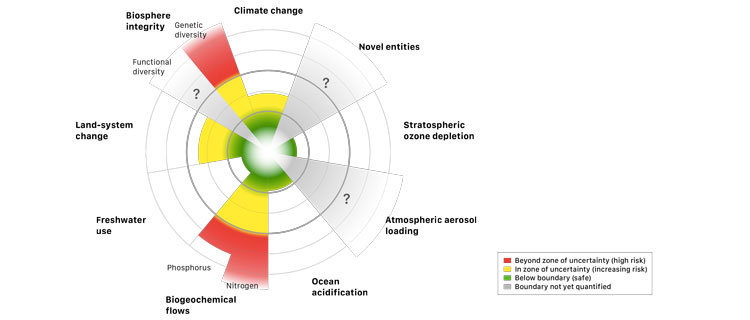
The [Planetary Boundaries] framework was first introduced in 2009, when a group of 28 internationally renowned scientists identified and quantified the first set of nine planetary boundaries within which humanity can continue to develop and thrive for generations to come. Crossing these boundaries could generate abrupt or irreversible environmental changes. Respecting the boundaries reduces the risks to human society of crossing these thresholds.
- Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
- Loss of biosphere integrity (biodiversity loss and extinctions)
- Chemical pollution and the release of novel entities
- Climate Change
- Ocean acidification
- Freshwater consumption and the global hydrological cycle
- Land system change
- Nitrogen and phosphorus flows to the biosphere and oceans
- Atmospheric aerosol loading
Here’s where the Center rates humanity with respect to each: